BASIC GEOMETRY CONCEPTS AN DEFINITION
Basic geometry: It's an area of knowledge which studies any elemets and operations on/in the planesuch as points, lines or shapes. It comes from greek, geo= ear and metry= mesurement.
Plane geometry= 3D plastric
- 1 dimension
- 2 dimension
Point: In geometry a point can defined as the place or location where two lines intersect. A point has not dimension, no height and no width
・good • bad + A x B ・C ⚪ D ⊕ E ⊹ F х good ✖️ bad
Linea: A on dimension oblect formad of infinite points. It has not and continuos on forever in a plane.
Ray: A live which begins at particular point (called the endpoint) and extens endlessly in one direction.
|––––––––––––– good
––––––+–––––– bad
–––––––––––––| good
Endpoint: And endpoint is a line segment or a ray ends or starts.
Line segment: It is a line with two endpoints.
A r
|------------- ray
A B
|------------| line segment
A
--+---------- line
Lenght: Measurement of something from end to end.
GEOMETRY DRAWING AND SUPPLIES CONCEPS AND DEFINITION
Freehand: Draw by hand without guiding instruments, measurements...
Line/technical drawing: It is a drawing mad with the help of suppies. It is usually the kind of drawing used for architecture or enginering.
Compass: It is a tool for drawing circles and arcs and also for measuring distance between points, consisting in two arms linked by a hinge.
Protactor: Am instrument for meauring a drawing angles on paper, usualy a flat semicircular transparent plastic sheet graduates in degrees.
Set square (UK) triangles (USA) : There are two special ruler with triangules shape. One is called the 45º triangle and other 60º/30º triangle. Both have 90º angle. They are used for making different angles.
Eraser: Use for eliminate the mistake.
Ruler: For making lines.
Line segment copyng: Griven the segment AB, copy it with the same lenght with a compas.
|--------------------|
|--------------------|
OPERATION WITH A SEGMENT
A B C D E F
|---------------| |----------| |----------------------|
A BC D
Addition: AB + CD |---------------|----------|
|--------------------------|
E D FC
Subtractiom: EF - CD |------------|----------|
|------------|
A BA B Multiply: AB X 3 |---------------|---------------|---------------|
|----------------------------------------------|
IMPORTANT DEFINITION ABOUT CIRCLES
Circle: Set of points at the same distance to a point called center.
Circunference: It is the full lenghts of a circle.
Center:It's a point equidistant to any points on a circle.
Radius:It's a lengh of a line segment from the center to this perimenter.
Diameter: A line segment that passes through the center and conects two points of a circles. Its lenght is double than the center.
Chor:A line segment wich conects two points of the circle not through the centre.
Arc:Segment of a circle.
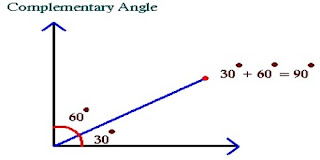
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS ABOUT ANGLES AND LINES
Paralles:They are two lines wich never intersect themselves so all their points are equidistant.
-------------------------
-------------------------
TYPES OF ANGLE
TYPES OF ANGLES (FORM)
Right:
Obtuse:
Acute:
Flat:
Complet:
Cero:
Operation with angles
Addition
Subtraction
Multiply
Divide a rect angle in 3 parts equals
The angle bisector (bisectriz): When I divide an angle into two equal parts.
Addition
Subtraction
Multiply
Divide a rect angle in 3 parts equals
The angle bisector (bisectriz): When I divide an angle into two equal parts.
Polygons
Number of side, name:
Triangle (3)
Quadrilaterals (4)
Pentagons (5)
Hexagons (6)
Heptagons (7)
Octagons (8)
Decagons (10)
Dodecagon (12)
Types
Concave
Convex
Star poligons
Regular
Irregular
Inscribed
Given the side
Other items
Elements
Side
Diagonal
Vertices
Altitud
Polygon
Star polygon: It is a particular polygon case with a star shape, created out of linking together non consecutive vertices of a regular polygon.
Inscribed Polygon: They are polygons place inside circles so all the verter of the polygon are placed on the circle.
Convex polygon: Any line draw through the polygon meets its boundary exactly twice.
Construction an equilateral triangle when I know the radius.
Do the right triangle when I know 1 side and the apothems.
Made right triangle when I know two sides.
Do the triangle when I know 3 sides.
Quadrilateral: They are polygons with four sides and fur angles.
- Parallelograms: They are quadrilateral with two sides of parallels apposite equal sides and and two pairs apposite equal angles.
- types
Trapeziums






























No comments:
Post a Comment